Causes and influencing factors of hydrogen embrittlement in steel
Hydrogen embrittlement is usually manifested as a significant decrease in the plasticity of steel, a sharp increase in brittleness, and a tendency to rupture after a period of time under static load. Hydrogen has a certain solubility in steel. During the steelmaking process, after the molten steel solidifies, a trace amount of hydrogen will remain in the steel. Steels are usually produced with a hydrogen content in a very small range. The solubility of hydrogen in steel decreases rapidly with decreasing temperature, and supersaturated hydrogen will be precipitated.
![]()
Factors Affecting Hydrogen Embrittlement Fracture of Steel
Envirnmental Factor
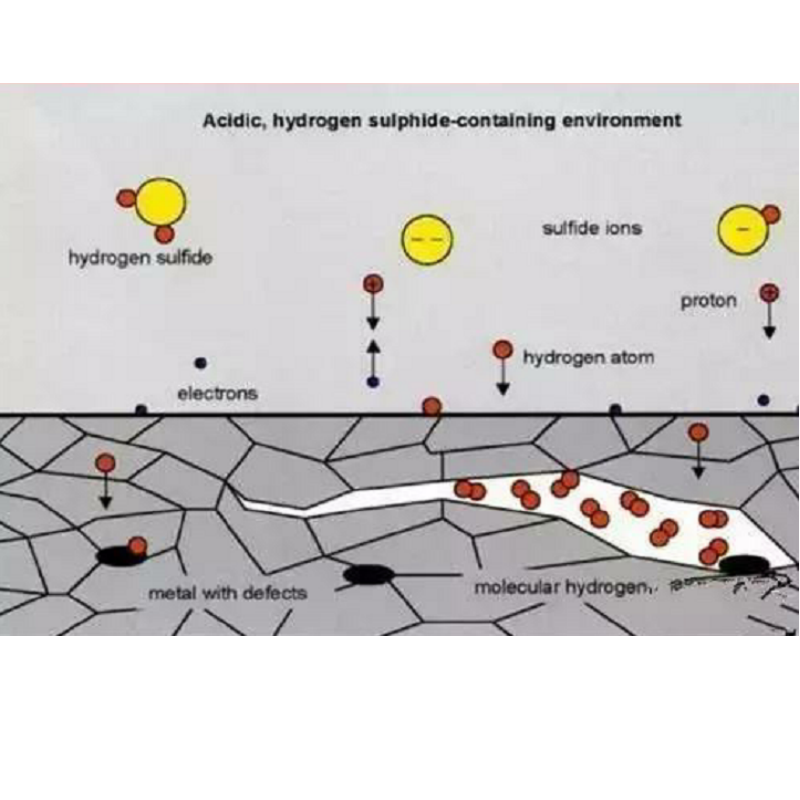
For example, when steel is in an environment with high hydrogen content, such as water, acid, and hydrogen, hydrogen diffuses through adsorption on the steel surface, causing the steel to become brittle. At the same time, the hydrogen partial pressure has a significant effect on the hydrogen crack growth rate, and increasing the hydrogen pressure will increase the hydrogen embrittlement susceptibility.

Strength Factor
In general, the higher the strength of the steel, the greater the susceptibility to hydrogen embrittlement. Some foreign developed countries expressly stipulate that "high-strength steel is not allowed to pickle" is to prevent hydrogen embrittlement. The chemical composition affects the hydrogen embrittlement fracture of steel through strength. This is because the segregation of hydrogen and S, P and other atoms at the grain boundary will weaken the bonding force of the grain boundary, thereby promoting the first fracture along the grain boundary.
heat treatment
The hydrogen embrittlement of steel is closely related to its microstructure and heat treatment. Experiments and facts show that the worse the thermodynamic stability of the structure, the greater the sensitivity of hydrogen embrittlement. For example, the hydrogen embrittlement tendency of pearlite and ferrite is much lower than that of martensite, and the high-carbon martensite with network distribution is the most sensitive.
Heat treatment measures to prevent hydrogen embrittlement
In the heat treatment industry chain, many processes require pickling, such as pickling after quenching before tempering, pickling before sandblasting after tempering, pickling before steam treatment or oxynitriding, pickling before surface strengthening such as TiN And pickling before electroplating, etc. The purpose of pickling is different at different stages, some are to remove oxide scale, some are to improve the surface activity of the workpiece, some are to reduce the size and so on. The traditional pickling process is cumbersome, long process, high cost, high energy consumption, serious pollution, poor working conditions, etc. What is even more terrifying is the great harm to the inherent quality of steel - hydrogen embrittlement. Therefore, improving the pickling process and taking measures to prevent hydrogen seepage have become the concerns of generations.
Improvement of pickling process
The rust on the surface of steel is mainly iron oxides and hydroxides, etc. The removal of these rust is mainly accomplished by the synergistic action of acid components with the help of surfactants, and the process of action is roughly dissolution and peeling. In order to overcome the defects brought by conventional pickling, the following improvements can be made.
First, reduce the acid concentration. The low-concentration pickling process has obvious economic and social benefits in reducing acid consumption, improving the environment and improving the surface quality of workpieces. The process utilizes the porosity of the oxide scale, and under the action of the wetting agent, the acid solution quickly penetrates into the interface between the substrate and the oxide scale for a chemical reaction, and the mechanical exfoliation effect of hydrogen is used to remove the oxide scale and clean the surface.
Secondly, the comprehensive characteristics of the mixed acid solution are utilized. In production, hydrochloric acid or sulfuric acid is commonly used to remove rust, but the performance of the two is different. If hydrochloric acid and sulfuric acid are prepared into a mixed solution in an appropriate proportion, they can have both functions, which can not only improve the speed of rust removal, but also reduce the operation time. temperature.
Finally, a special pickling process is used. Different pickling processes are adopted for different workpiece shapes, uses and heat treatment states, which means that the pickling process should also be individualized.
Measures to prevent hydrogen embrittlement
The hydrogen permeation in the pickling process is a rather complicated process, which involves the conjugation step of corrosion, and the parallel and series steps of hydrogen adsorption and precipitation on the metal surface and immersion inside the metal, as well as the deep-seated problem of stress corrosion. . The research shows that directly carrying out the electrochemical measurement of hydrogen permeation is a feasible method to study the hydrogen permeation behavior during the pickling process under the pickling condition. In order to reduce the degree of hydrogen permeation of steel parts, the following measures can be taken to prevent hydrogen permeation.
First, the introduction of multifunctional slow inhibition. The multifunctional inhibitor has the functions of corrosion inhibition and fog inhibition, not only the pickling speed is fast, but also the function of inhibiting hydrogen permeation is strong, and the corrosion inhibition rate is high.
Second, prevent metal impurities from contaminating the pickling solution. It has been found out that when the pickling solution contains P, As, Sn, Hg, Pb, Zn, Cd and other metal impurities, it will promote the increase of hydrogen permeation and aggravate the tendency of hydrogen embrittlement fracture.
Third, the hydrogen drive treatment. It is best to carry out hydrogen flooding treatment at 180~200°C × 3~4h for all workpieces that have been pickled.








